






Vitamin B3, or niacinamide, can assist with skin conditions. It reduces inflammation, strengthens the skin barrier, and regulates oil production, benefiting conditions like eczema and acne. Niacinamide promotes cell rejuvenation, collagen production, and has anti-inflammatory properties. It supports the skin's barrier function and improves texture. The recommended daily allowance for niacin is approximately 16 mg for adult males, but higher doses can enhance skin health. Understand potential side effects and consult a healthcare provider. Consider incorporating niacinamide in skincare or through diet for best results. Optimizing skin health with Vitamin B3 is crucial for various skin concerns.
Key Takeaways
- Vitamin B3, or niacinamide, reduces inflammation and strengthens the skin barrier for eczema relief.
- Niacinamide regulates oil production, reduces acne-causing bacteria, and calms redness for acne treatment.
- Niacinamide promotes collagen production, cellular rejuvenation, and improves skin texture and elasticity.
- Recommended dosages range from 16 mg to 500 mg per day for skin health benefits.
- Potential side effects include liver problems, gastrointestinal issues, and skin flushing with high doses.
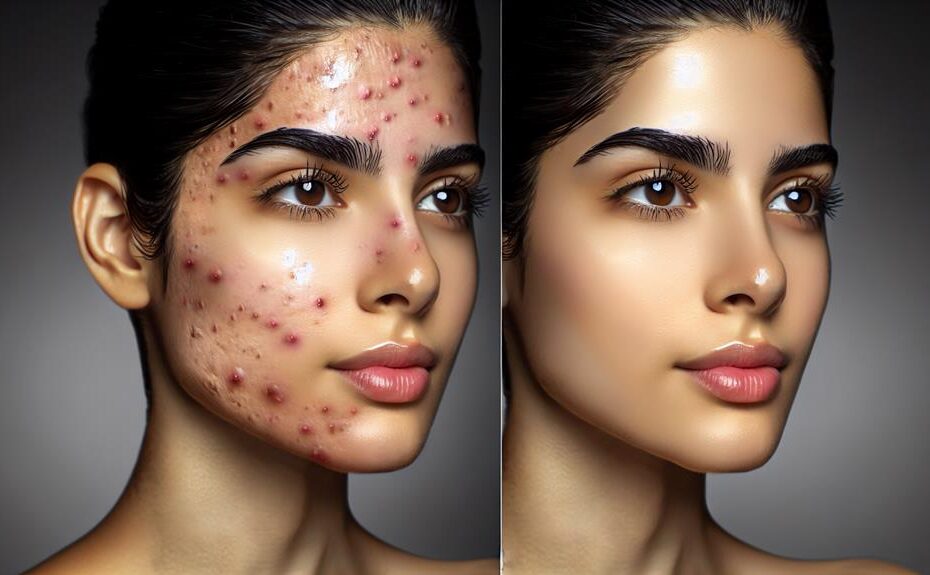
Skin Conditions Benefitted by Vitamin B3
When considering the skin conditions benefitted by Vitamin B3, it is essential to understand the specific mechanisms at play. Vitamin B3, also known as niacinamide, has shown promising results in providing relief for eczema and treating acne. Eczema, a common skin condition characterized by red, itchy patches, can benefit from the pivotal properties of Vitamin B3. By reducing inflammation, Vitamin B3 helps alleviate the symptoms associated with eczema, such as itching and irritation. Additionally, Vitamin B3 has been found to strengthen the skin barrier, which is often compromised in individuals with eczema, leading to improved skin health and reduced flare-ups.
In the case of acne treatment, Vitamin B3 plays a vital role in regulating oil production and reducing the proliferation of acne-causing bacteria on the skin. Its anti-inflammatory properties also help in calming redness and swelling associated with acne breakouts, promoting faster healing and preventing future blemishes. Incorporating Vitamin B3 into skincare routines has shown promising results in improving overall skin condition for individuals struggling with acne.
Mechanism of Action in Skin
Vitamin B3, or niacinamide, exerts its beneficial effects on the skin through intricate molecular pathways that enhance skin health and address various dermatological concerns. Niacinamide plays a pivotal role in promoting cellular rejuvenation by aiding in the production of essential skin proteins like collagen. This process helps maintain skin elasticity and firmness, reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
Additionally, niacinamide exhibits anti-inflammatory properties, which can help alleviate redness, sensitivity, and inflammation associated with conditions like acne and rosacea. By calming the skin, niacinamide supports the skin's barrier function, which is essential for protecting against environmental aggressors and maintaining peak hydration levels. Moreover, niacinamide has been shown to regulate sebum production, making it beneficial for individuals with oily or acne-prone skin.
Niacinamide Vs. Nicotinamide

Comparing niacinamide and nicotinamide reveals subtle differences in their molecular structures and biological activities. Niacinamide, also known as nicotinamide, is a water-soluble form of vitamin B3 that offers various benefits for skin health. Niacinamide is a key component in skincare products due to its ability to improve the skin's barrier function, decrease inflammation, regulate oil production, and reduce hyperpigmentation. On the other hand, nicotinamide, the amide form of niacin (vitamin B3), is essential for the body's energy production and DNA repair processes. While both niacinamide and nicotinamide are forms of vitamin B3, niacinamide is specifically favored in skincare formulations for its skin-enhancing properties. Niacinamide benefits the skin by enhancing its elasticity, improving texture, and reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. Understanding the differences between niacinamide and nicotinamide can help individuals choose the most suitable form of vitamin B3 for their skincare needs.
Dosage Recommendations for Skin Health
For peak skin health, consider the recommended dosage of vitamin B3 to effectively address various skin conditions. Niacinamide, a form of vitamin B3, can be obtained through dietary sources like meat, fish, and nuts. However, for targeted skin benefits, supplements or topical applications may be necessary.
The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for niacin, which includes niacinamide, is around 16 mg per day for adult males and 14 mg per day for adult females. When it comes to specific skin conditions, higher doses ranging from 200-500 mg per day have been used in studies to improve skin health and appearance.
In topical applications, niacinamide concentrations typically range from 2-10% in over-the-counter creams. However, for more severe skin conditions, dermatologists may recommend products with higher concentrations for better efficacy.
Consulting with a healthcare provider or dermatologist is advisable to determine the appropriate dosage of vitamin B3 for your skin concerns. Balancing dietary intake with supplements or targeted topical treatments can help optimize the benefits of vitamin B3 for your skin health.
Potential Side Effects to Consider
Consider potential side effects that may arise when utilizing vitamin B3 for skin health to guarantee a thorough understanding of its impact on your well-being. While vitamin B3, also known as niacinamide, is generally important, there are some considerations to keep in mind. Long-term use of high doses of vitamin B3 can lead to side effects such as liver problems, gastrointestinal issues, and skin flushing. It is essential to adhere to recommended dosages to minimize these risks.
Allergic reactions to vitamin B3 are rare but possible. If you experience symptoms like itching, swelling, dizziness, or trouble breathing after taking vitamin B3, seek immediate medical attention. Additionally, individuals with liver disease, kidney disease, or diabetes should consult a healthcare provider before starting vitamin B3 supplementation to prevent adverse effects on these conditions.
Precautions should be taken to avoid exceeding the recommended daily intake of vitamin B3 to minimize the likelihood of side effects. While vitamin B3 offers numerous benefits for skin health, understanding and being aware of potential risks is essential for safe and effective supplementation.
Tips for Incorporating Vitamin B3
To effectively incorporate vitamin B3 into your skincare routine, make sure you follow these practical tips for best results. When it comes to skincare routines, consider adding niacinamide supplements to your daily regimen. Niacinamide, a form of vitamin B3, has shown promising results in improving skin barrier function and reducing inflammation. Incorporating dietary sources rich in vitamin B3, such as poultry, fish, and nuts, can also support skin health from within.
In addition to supplements and dietary sources, topical applications of niacinamide can be beneficial for addressing specific skin concerns. Look for skincare products containing niacinamide and incorporate them into your daily skincare routine. Niacinamide has been found to help with various skin conditions like acne, hyperpigmentation, and fine lines.
Remember to patch test new products to guarantee compatibility with your skin. Consistency is key when incorporating vitamin B3 into your skincare routine, so be patient and give it time to show results. By integrating niacinamide through both internal supplements and external applications, you can potentially enhance the overall health and appearance of your skin.




