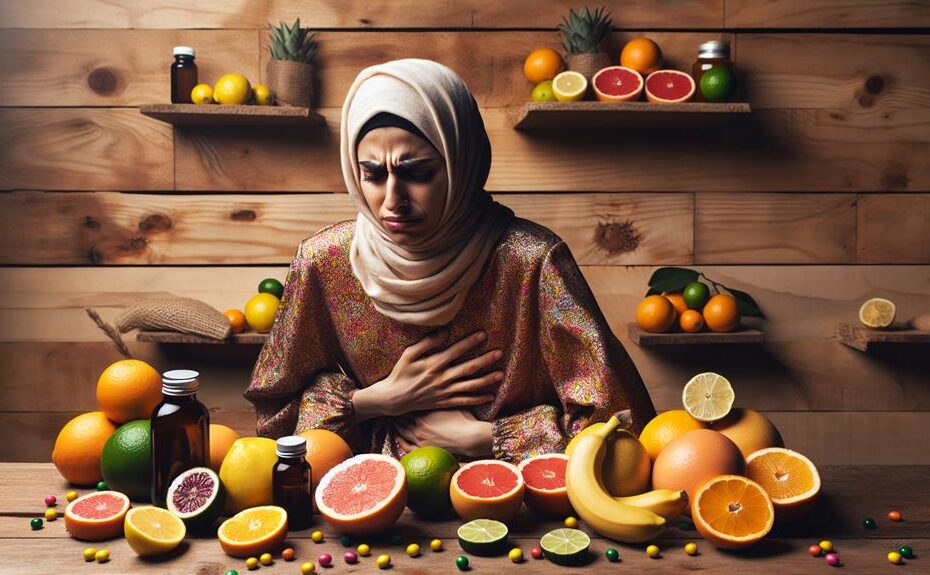







Excess vitamin C intake can impact your digestion, leading to stomach cramps, diarrhea, and gut inflammation. It may disrupt food breakdown and nutrient absorption. Consider sticking to daily adult recommended doses (75-90mg) for digestive balance. Absorption primarily occurs in the small intestine, affected by gut health and function. High vitamin C intake can increase stomach acidity, potentially causing discomfort like acid reflux. Hydration and balancing electrolytes are key to managing related diarrhea symptoms. To optimize absorption, pair vitamin C with non-heme iron sources and seek professional advice for personalized recommendations.
Key Takeaways
- Excessive Vitamin C can cause stomach cramps and diarrhea.
- Gut inflammation may lead to discomfort like cramps and bloating.
- Vitamin C disrupts normal food breakdown and nutrient absorption.
- High doses can increase stomach acidity, potentially causing reflux.
- Osmotic effect of Vitamin C can contribute to diarrhea symptoms.
Potential Digestive Side Effects
Excessive intake of Vitamin C can lead to potential digestive side effects, such as stomach cramps and diarrhea. While Vitamin C is vital for overall health, consuming it in excess may pose risks to your gut health. One concern is the potential for gut inflammation, which can be exacerbated by high levels of Vitamin C. This inflammation may lead to discomfort such as stomach cramps and bloating, impacting your overall digestive well-being.
Moreover, excessive Vitamin C intake can interact with digestive enzymes in your system. These interactions may disrupt the normal breakdown of food and absorption of nutrients, potentially causing digestive issues like diarrhea. It is important to be mindful of your Vitamin C intake and make sure it aligns with recommended daily allowances to prevent these unwanted side effects.
Recommended Vitamin C Dosage
For prime health benefits, it is important to take into account the suggested daily dosage of Vitamin C. Vitamin C interactions and absorption play a significant role in determining the ideal intake. The recommended daily allowance of Vitamin C for adults is around 75 to 90 milligrams for women and men, respectively. However, some studies suggest that higher doses, up to 2000 milligrams per day, can provide additional benefits, especially for individuals under high oxidative stress or smokers.
When deciding on your Vitamin C dosage, it is essential to take into consideration your individual health needs, as excessive intake can lead to gastrointestinal disturbances like diarrhea. Vitamin C is water-soluble, meaning the body does not store it, so it is generally considered safe even at higher doses. The benefits of Vitamin C supplementation include enhanced immune function, improved skin health, and better absorption of iron from plant-based sources. Consulting with a healthcare provider can help you determine the most suitable Vitamin C dosage for your specific health requirements.
Absorption Process in the Gut
Understanding how Vitamin C is absorbed in the gut is essential for maximizing its benefits and avoiding potential digestive issues. In the gut, specifically in the small intestine, Vitamin C is absorbed through both active transport and passive diffusion. Active transport involves the use of specific proteins to carry Vitamin C across the intestinal wall, ensuring efficient absorption. On the other hand, passive diffusion allows Vitamin C to move across the intestinal membrane based on concentration differences.
Gut health plays a critical role in the absorption of Vitamin C. A healthy gut lining with intact epithelial cells promotes best nutrient absorption, including Vitamin C. Nutrient absorption is a complex process influenced by various factors such as the presence of other nutrients, gut motility, and overall digestive health. Ensuring a well-balanced diet rich in Vitamin C-containing foods can support the absorption process and contribute to overall health. Maintaining gut health through a diverse and nutritious diet is key to maximizing the benefits of Vitamin C intake.
Impact on Stomach Acid Levels
Maintaining ideal stomach acid levels is important for the proper digestion and absorption of nutrients, including Vitamin C. When excessive Vitamin C is consumed, it can potentially lead to an overly acidic environment in the stomach. While Vitamin C itself is not acidic, it can stimulate the production of gastric acid, which lowers the pH of the stomach. This increased acidity may cause gastric discomfort in some individuals.
The stomach normally maintains a delicate balance of acidity to break down food and absorb nutrients effectively. However, too much Vitamin C can disrupt this balance, leading to symptoms like acid reflux, heartburn, or stomach cramps. Individuals with conditions like gastritis or peptic ulcers may be particularly sensitive to changes in stomach acid levels caused by excessive Vitamin C intake. Being mindful of your Vitamin C consumption and consulting a healthcare provider if you experience persistent gastric discomfort or digestive issues is important. Balancing your nutrient intake is vital for supporting good digestion and overall health.
Connection to Diarrhea Symptoms

Have you ever wondered how excessive Vitamin C intake may be connected to diarrhea symptoms? When consumed in large amounts, Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, can lead to digestive issues such as diarrhea. This is primarily due to Vitamin C's osmotic effect in the gastrointestinal tract, drawing water into the intestines and potentially causing loose stools.
To mitigate diarrhea symptoms associated with excessive Vitamin C intake, it is essential to focus on maintaining adequate hydration levels and electrolyte balance. Diarrhea can lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances, so increasing fluid intake and consuming electrolyte-rich foods or beverages is vital.
Moreover, paying attention to your fiber intake and overall gut health is key. Fiber plays a significant role in digestive health and can help regulate bowel movements. By incorporating fiber-rich foods into your diet, you can support gut function and potentially alleviate diarrhea symptoms caused by excessive Vitamin C consumption.
Balancing your intake of Vitamin C with proper hydration, electrolytes, fiber, and gut health considerations can help minimize the likelihood of experiencing diarrhea as a result of excessive Vitamin C intake.
Role in Gut Microbiota Balance
Excessive intake of Vitamin C can influence the balance of gut microbiota, impacting overall digestive health and function. Vitamin C plays a vital role in maintaining gut health balance by influencing the diversity of the microbiome. The gut microbiota consists of trillions of microorganisms that are essential for digestion, immune function, and overall well-being. When there is an imbalance in the gut microbiota, it can lead to various digestive issues such as bloating, gas, and irregular bowel movements.
Research suggests that Vitamin C can act as a prebiotic, promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut. By supporting the growth of these good bacteria, Vitamin C helps maintain microbiome diversity, which is essential for well gut health. A balanced gut microbiota is associated with better nutrient absorption, improved immune function, and reduced risk of digestive disorders.
Therefore, ensuring an adequate intake of Vitamin C through a balanced diet can contribute to a healthy gut microbiota, supporting overall digestive health and function.
Risk Factors for Digestive Upset

To prevent digestive upset, understanding the risk factors that can disrupt gut health is essential for maintaining overall well-being. Two key risk factors for digestive upset are dietary habits and hydration levels. Dietary habits play a vital role in digestion. Consuming excessive amounts of processed foods, high in fats and sugars, can lead to digestive issues. On the other hand, a diet rich in fiber from fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can promote healthy digestion. Hydration levels also play a major role in gut health. Inadequate water intake can cause constipation and hinder the proper functioning of the digestive system.
Moreover, excessive intake of certain substances like caffeine and alcohol can also irritate the digestive tract. It is important to be mindful of how these substances affect your digestive system and adjust your intake accordingly. By paying attention to your dietary habits and ensuring adequate hydration levels, you can greatly reduce the risk of experiencing digestive upset.
Combining Vitamin C With Food
Maintaining a balanced approach to incorporating Vitamin C with your meals can optimize its absorption and potential benefits for your overall health. Food interactions play an important role in how well your body absorbs Vitamin C. Pairing Vitamin C-rich foods with sources of non-heme iron, like leafy greens or legumes, can enhance iron absorption due to the vitamin's acidic nature. However, it's vital to be careful with high doses of Vitamin C supplements on an empty stomach, as they may lead to digestive discomfort in some individuals.
Optimal timing is also key when combining Vitamin C with food. Consuming Vitamin C during meals or shortly before can aid in the absorption of non-heme iron and enhance the overall nutritional value of the meal. Additionally, spreading Vitamin C intake throughout the day can help maintain steady levels in your body. Remember, a well-rounded diet with a variety of nutrients is crucial for overall health, and incorporating Vitamin C strategically can be a beneficial part of your dietary routine.
Seeking Professional Advice

When considering the impact of Vitamin C on your digestion, seeking advice from a healthcare professional can provide valuable insights tailored to your individual needs and health status. Nutritional counseling from experts can help you understand how excessive Vitamin C intake may affect your digestive health. Healthcare professionals, such as dietitians or doctors, can offer expert opinions on whether your current Vitamin C consumption aligns with recommended levels and how it may be influencing your digestion. Through their guidance, you can make informed dietary adjustments to optimize your digestive health while ensuring you are not overloading your system with Vitamin C. These professionals can consider your overall health, any existing conditions, and potential interactions with medications to provide personalized recommendations. By seeking professional advice, you can navigate the complexities of Vitamin C intake and its impact on digestion more effectively, leading to a balanced approach to your nutritional needs and overall well-being.





